1. Architecting Security and Governance Across your AWS Environment, Protected by an Integrated AWS Identity and Access Management
Multi-account environments
- Different accounts for different purposes with different access rights, usage limits, etc.
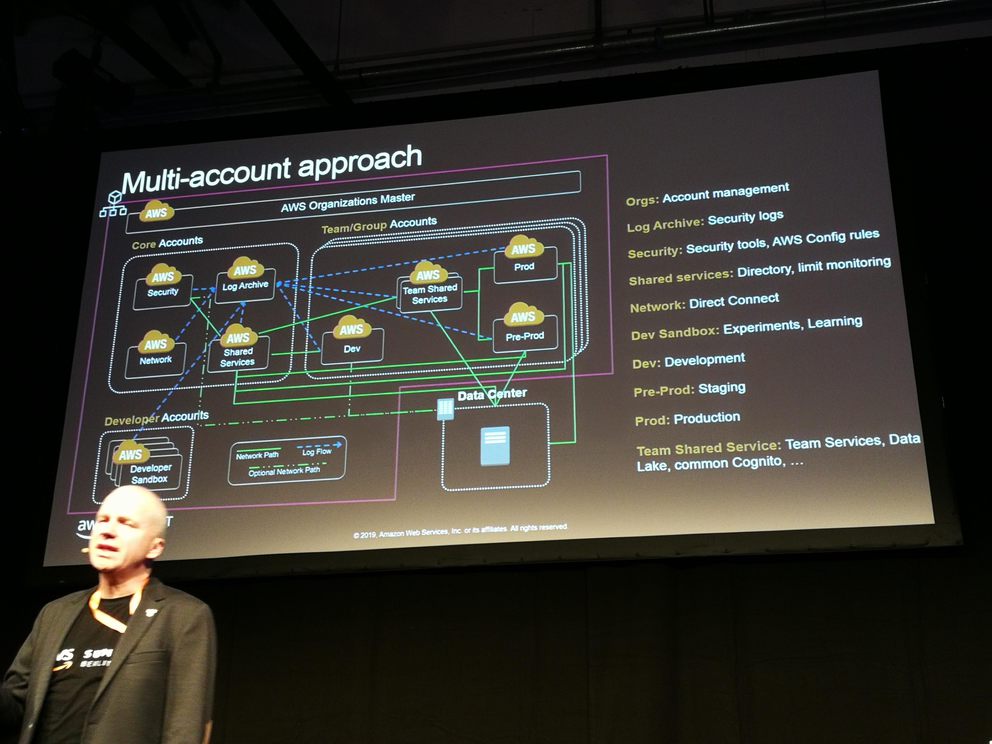 -
-
- Every account should have the following services enabled: AWS CloudTrail, AWS Config, Amazon Guard Duty
- AWS Landing Zone
- Automated setup of a multi-account environment (based on best practices)
- Some services already set up in specific accounts
- Account vending machine
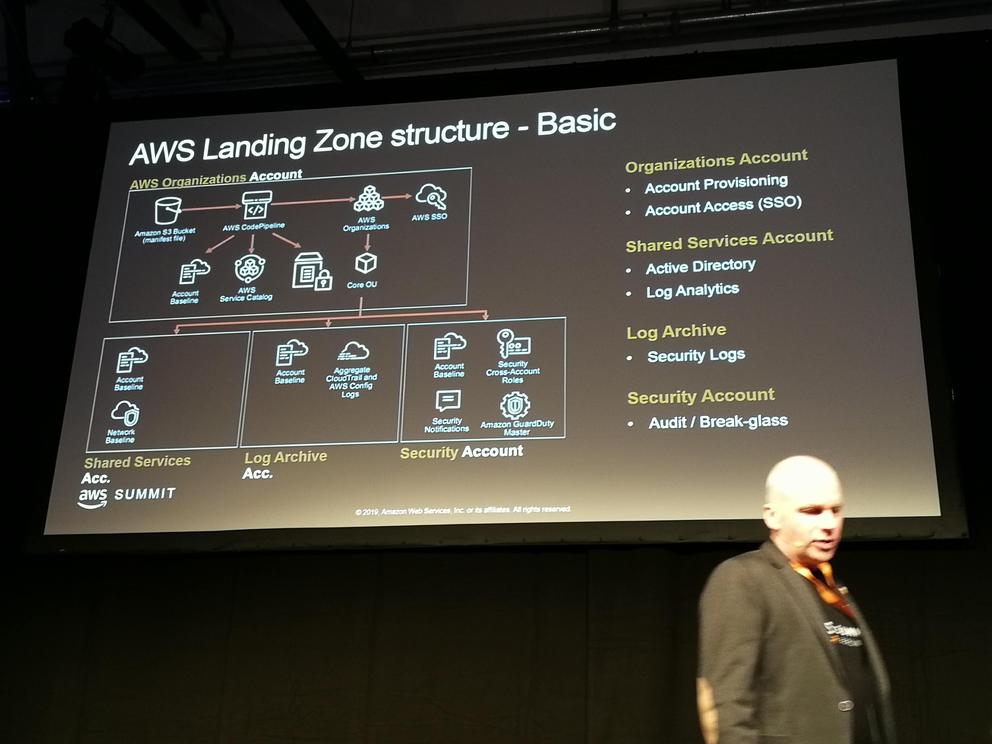
- AWS Control Tower (currently in preview)
- Similar to AWS Landing Zone
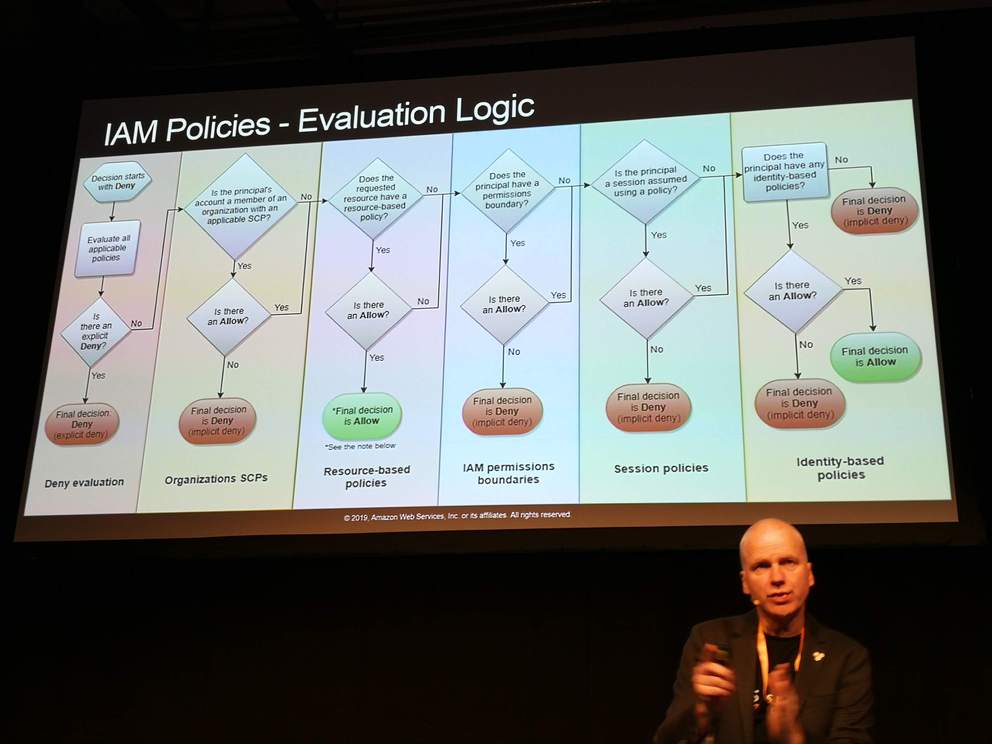
Access management in multi-account environment
- Service Control Policies (SCP) (vs. IAM policies)
- Assign SCPs to organizational units (OU)
- Manage access to AWS services) (vs. manage access to ARNs in IAM)
- By default, everything is allowed (vs. everything denied in IAM)
- Assigned to oganizational units or accounts (vs. roles and groups in IAM)
Combine IAM policies and SCPs
- The effective permissions ar the intersections of all IAM policies and SCPs
2. Cutting-Edge Architectures Based on AppSync, Lambda, and Fargate
New AWS services for general-purpose applications since 2009
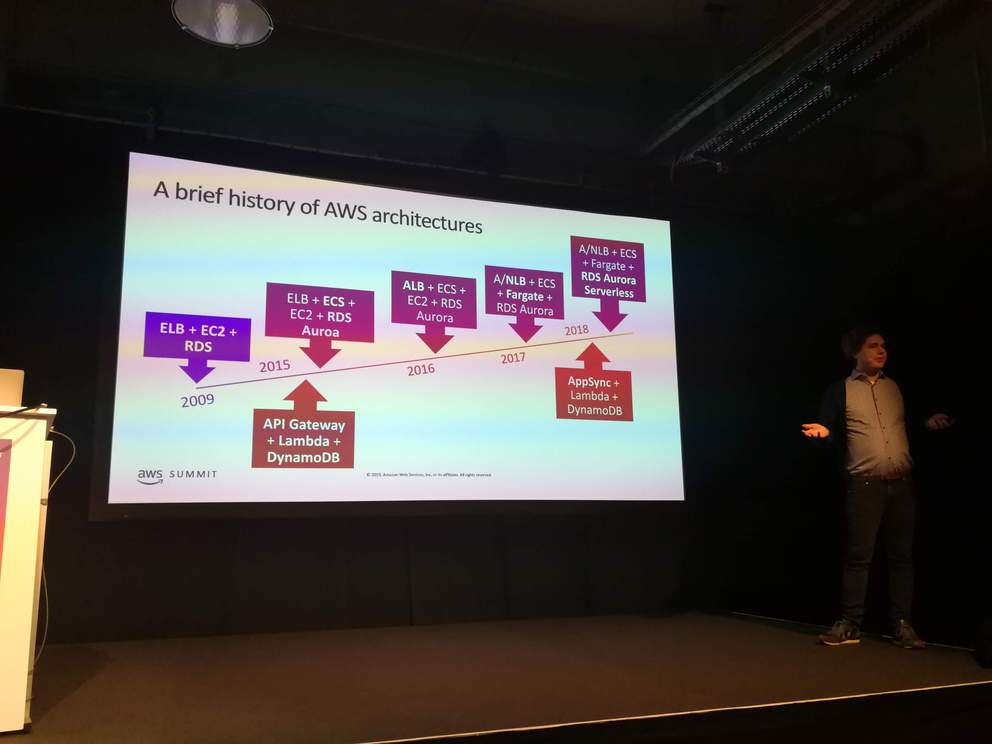
Architecture 1: AppSync - Lambda - DynamoDB
- AppSync: like API Gateway, but for GraphQL APIs instead of REST APIs
- Requires authorisation including Cognito, IAM, API keys, and Open ID Connect
- Easier to use than API Gateway
- GraphQL
- Schemas for defining the API
- Two main types of calls: Query and Mutation
- Define types of all objects going through API
- Connect data sources (e.g. DynamoDB, Lambda)
Architecture 2: Application Load Balancer - Fargate - Aurora
- Fargate
- Specify Docker image to run, and Fargate runs it
- Allows auto-scaling of containers (replicas)
- Part of ECS
- Use it if it’s not really necessary to used ECS or EKS (to avoid the heavy lifting associated with them)
- Combine with CloudMap (service discovery)
CI/CD
- Use Code Pipeline and CodeBuild to build code on push to GitHub repository and then deploy as changes to a CloudFormation template
3. From Idea to Customers: Developing Modern Cloud-Enabled Apps with AWS
- ReactNative translation app in 95 lines of code
- Amplify, AppSync, Amazon Translate, Polly, S3
- GraphQL
- Main objects: queries, mutations, subscriptions (real-time data pushed to subscribed clients)
- Client specifies shape of response (no need to make multiple requests to get a specific set of data)
- AppSync
- Managed GraphQL service
- Real-time and offline capabilities
- Amplify
- Create, read, update, and delete services for use in an application
- Amplify CLI
- Generates and applies CloudFormation templates
amplify add <...>: updates CloudFormation templateamplify push: applies CloudFormation template
- Generates and applies CloudFormation templates
- JavaScript library
- For accessing services created by Amplify CLI
- Questions
- Where can CloudFormation template generated by Amplify CLI be found? Can it be used without Amplify CLI?
- Amazon Pinpoint
- Collect and analyses application usage metrics
- Engage users with email, SMS, etc.
- Agent code integrated into applications (can be done with Amplify)
4. Managing All Your Operations in One Tool
Resource groups
- Part of AWS Systems Manager
- Create groups of resources within an application
- Specification of resources
- Based on tags
- Based on CloudFormation stacks (queries on CloudFormation stacks)
- Groups are dynamic (if tags or CloudFormation stacks are updated, resource groups are updated too)
Where can resource groups be used?
- AWS Config
- Create compliance rules on resource groups
- View configuration changes in resource groups
- CloudTrail
- Show all API calls in account
- AWS Personal Health Dashboard
- See if failure is caused by application or AWS
- AWS Trusted Advisor
- Inventory
- Part of AWS Systems Manager
- CloudWatch Dashboards
- Filter based on resource groups
- Built-In Insights
- Part of AWS Systems Manager
Taking action on identified issues

- AWS Systems Manager
- Automation
- Convert repetitive tasks into runbooks
- Run Commands
- Run commands on instances
- Session Manager
- Connect to instance without having to open TCP ports or installing SSH keys on the instances
- State Manager
- Enforce OS configurations on instances
- Automation
5. Leveraging AWS Marketplace: Sell Your Application the Way Customers Want to Buy

- Sell applications that buyers can install in their own AWS account (with a single click)
- Alternative to on-premises software vendings
- Not an alternative to SaaS solutions that run completely on the seller’s infrastructure
- Delivery methods
- AMI, Amazon SageMaker (new), container (new), SaaS, API
- Purchasing methods
- Free trial, pay-as-you-go, monthly, yearly, etc.
- Provides standard legal terms, etc.
6. Full Stack in the Era of Serverless Computing
- What is serverless?
- Service-full
- External services constitute the building blocks of a system
- Try to use external services as much as possible
- Codeless
- Merging of engineering roles
Amplify
- Components
- CLI
-
Configure and launch a set of services

-
- Client library
- Interact with cloud services
- Pre-configured components for popular front-end frameworks (Vue, Angular, React Native)
- CI/CD
- CLI
- Supports multiple environments, like dev, prod, etc. (new)
- Creates
amplify/backendfolder- Containing a sub-folder for each added service
- If using a GraphQL API (with AppSync), also cretes the local GraphQL objects (queries, mutations, subscriptions)
6. Extending EKS with Open-Source Tools
- AMI build scripts
- eksctl
- By default puts all worker nodes in a public subnet (can be changed with
--node-private-networking)
- By default puts all worker nodes in a public subnet (can be changed with
- Helm
- Package repository of Kubernetes applications
- Needs to install Tiller pod in cluster
helm init
- Need to create servie account and cluster role for Tiller pod
- When Tiller is installed, can install application with
helm install - Helm chart may store passwords in a Kubernetes secret
- Pod-level permissions
- By default pod inherit permissions of worker node instance role
- All pods running on a host have the same permissiosn
- Two tools for container-specific permissions: kiam and kube2iam
- kube2iam runs a pod on each worker node (in kube-system namespace)
- This pod configures iptables on the host
- By default, denies any access to outside services
- Specify pod permissions with annotations in the pod definitions (reference an IAM role)
- Also possible to add this annotation to a namespace definition and every pod running in this namespace will inherit it
- kube2iam requires an IAM role itself
- Install kube2iam with Helm
- By default pod inherit permissions of worker node instance role
- Cluster AutoScaler
- Runs pod in the kube-system namespace
- Automatically launches worker nodes (as well as pods)
- https://gitlab.com/ric_harvey/bl_eks_opensource
7. Microservices on AWS: Architectural Patterns and Best Practices
- Building blocks for a microservices architecture: ECS, EKS, Fargate, Lambda
- Decision diagram which service to use:
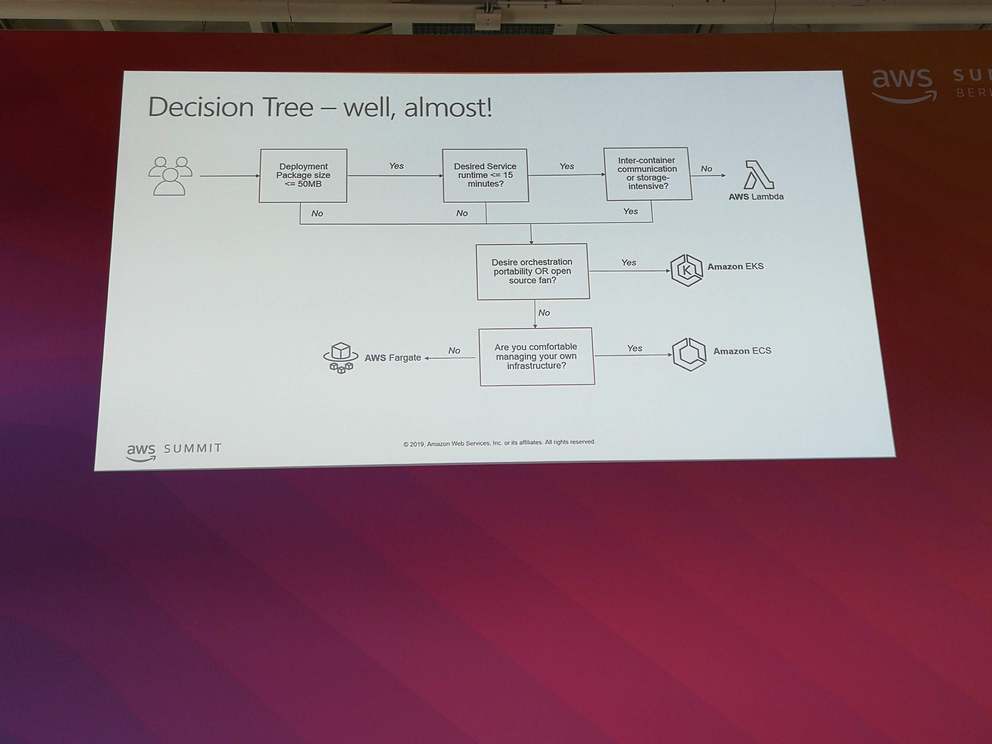
- Start with Lambda and only use containers if really needed
Best practices
- Reduce size of Docker images
- Use Busybox base image
- Problem: each instruction in a Docker file adds a layer to the image
- Use multi-stage Docker builds
- Copy just parts of a previous stage to the target image in a the current stage
- In Kubernetes, optimize pods
- Avoid sidecar containers if possible
- Use resource constraints in pod definitions (requests and limits)
- Lambda Layers
- Upload code to Lambda and reference it from multiple Lambda functions
- Lambda custom runtimes are implemented with Lambda Layers
- Lambda Container Image Converter
- Convert Docker images to Lambda Layer (and upload it to Lambda)
- https://github.com/awslabs/aws-lambda-container-image-converter
8. AWS Networking Advanced Concepts and New Capabilities
- Two account and VPC strategies
- Few large accounts and VPCs
- Key decisions: IAM (policies)
- Many small accounts and VPCs
- Key decisions: infrastructure and networking
- Few large accounts and VPCs
- Multi VPC strategies
- Subnets (public, private)
- ACLs
- Separate VPCs
- VPC Sharing: share subnets in a VPC with other accounts
- Allows to use a separate account for managing all the networking infrastructure used by other accounts
- Shared Services: use a service in all VPCs
- VPC peering (one-to-one connectivity)
- AWS PrivateLink
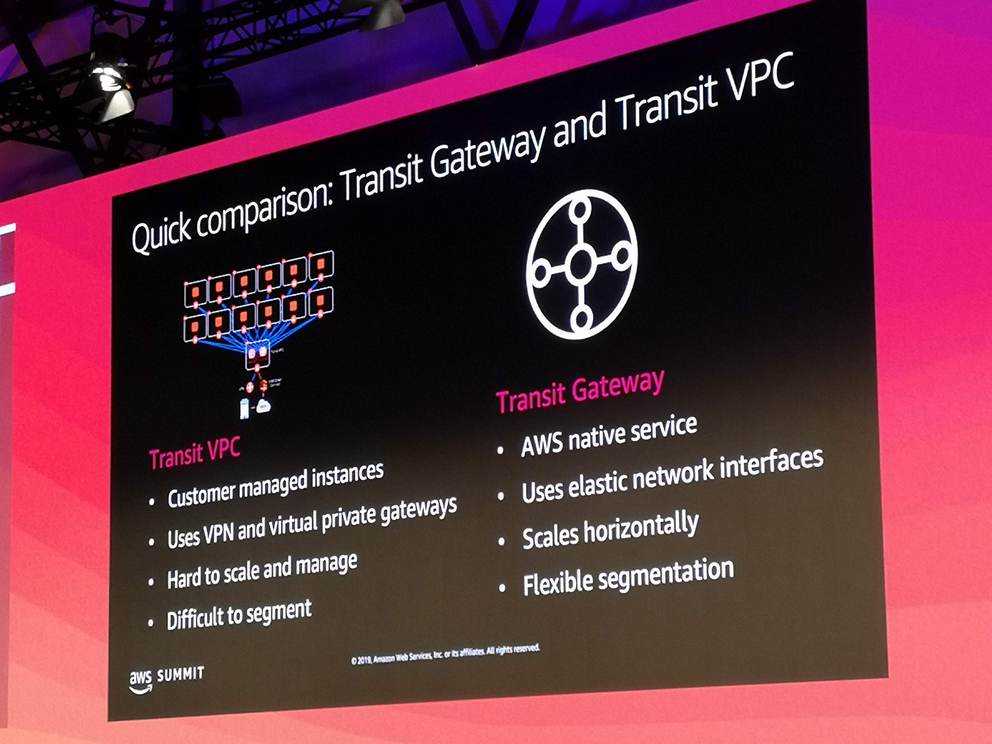
- Transit VPC
- An additional VPC for routing traffic between VPCs
- Requires EC2 instances (in Transit VPC)
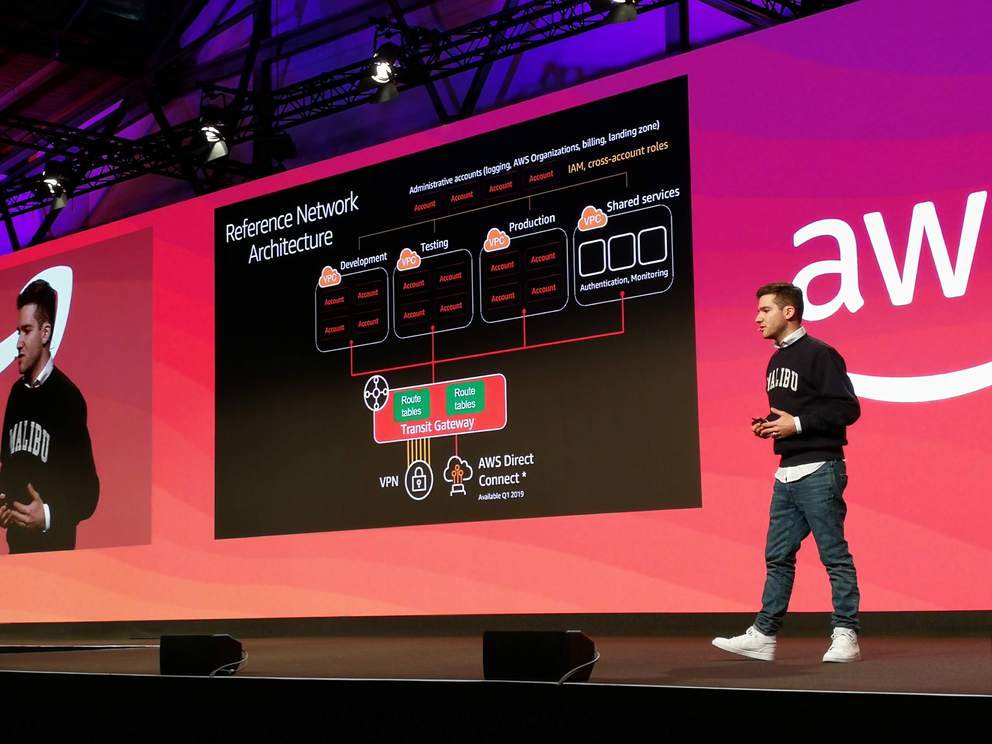
- API Transit Gateway
- Connect VPCs to Transit Gateway so they can talk to each other
- Connectivity can be fully configured with routing domains and routes
- Transit Gateway can also be connected to VPN or AWS DirectConnect

- AWS Global Accelerator
- Like CloudFront, but for any type of applications (not just HTTP)
- Provides single global IP, which routes traffice to application in nearest region
9. Handling Heterogeneous Container Clusters in AWS
- Computing infrastructure of Scout 24
- One separate AWS account (platform account) with an ECS cluster where all the services run
- Separate accounts for each product
- Product accounts need to deploy serivces to platform account
- CloudFormation stack triggering SNS message to topic of platform account
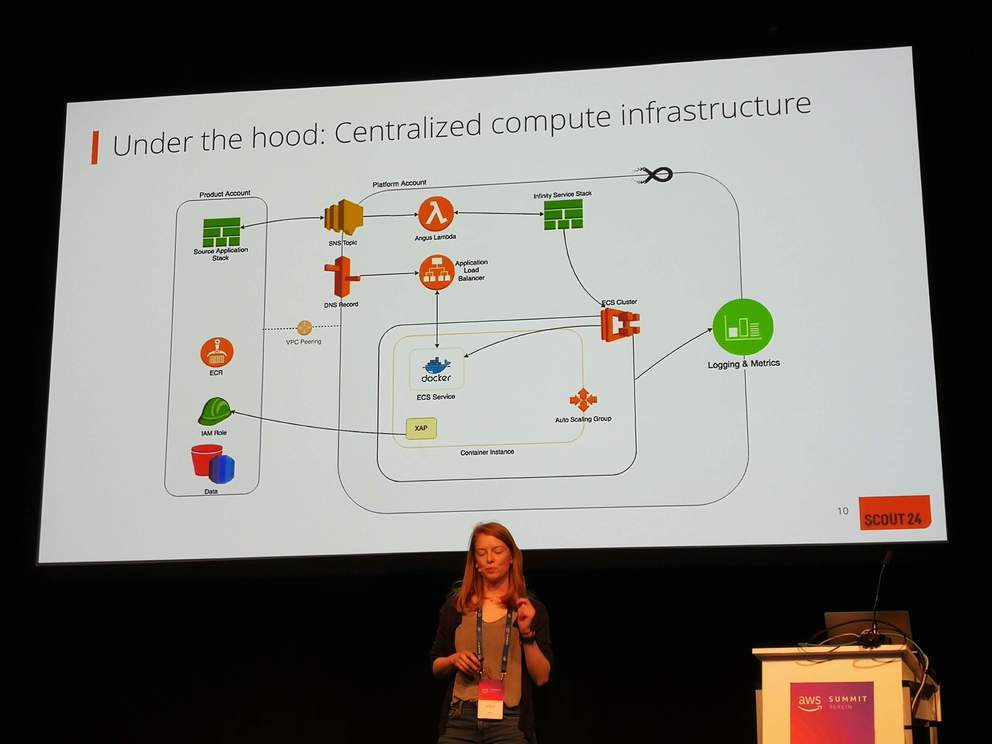
- Problems of having heterogenous services on an ECS cluster
- Declared and effective CPU usage may conflict
- CloudFormation not suited to deploy to ECS, use ECS API or CodeDeploy
- ECS does not have as many tools as EKS
- Kubernetes (EKS) handles heterogeneous workloads better
10. Boost your AWS Infrastructure
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
- Benefits of IaC
- Automated, repeatable, versioned
- IaC approaches
- Declarative: CloudFormation templates
- Imperative: Cloud Development Kit (CDK), Troposphere, SparkleFormation, GoFomration
- All these tools generate CloudFormation templates
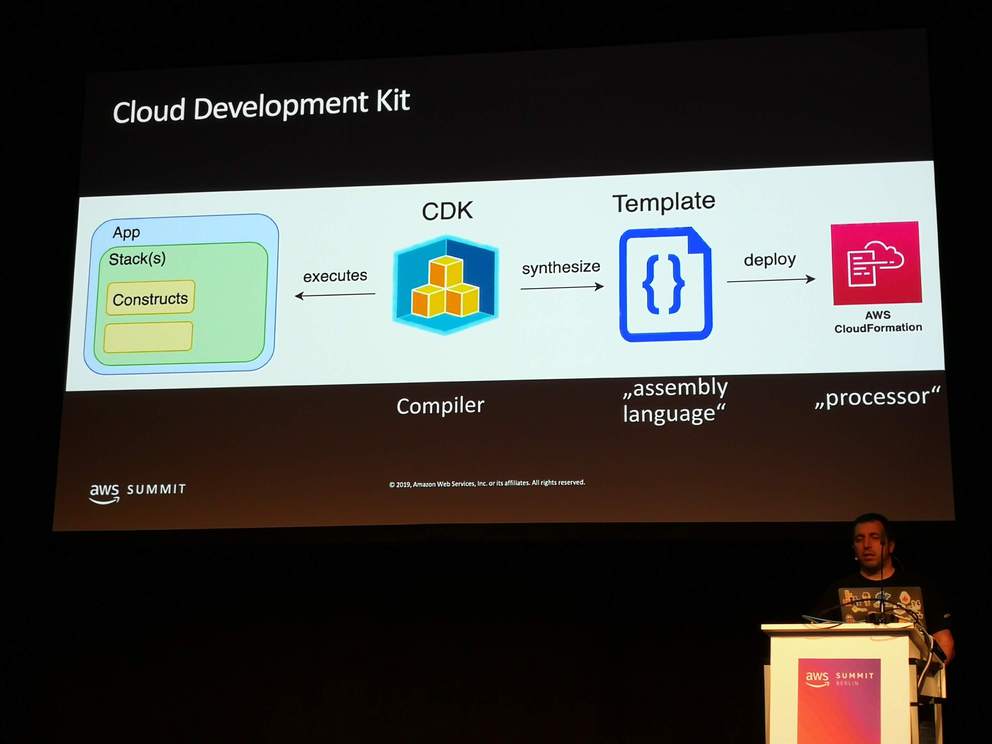
Cloud Development Kit (CDK)
- Currently in beta
- Components
- Apps: executable programs that produce CloudFormation templates
- Stacks: deployable units (corresponding to CloudFormation stacks)
- Constructs: resources sets to be used as subsystems of a stack
- Basic resources
- AWS Construct Library (predefined resource sets on AWS service level following best practices)
- Custom (resource sets that can be defined by user and reused)
- Command-line tool
cdk initcdk synthesize(generate CloudFormation template)cdk deploy(apply CloudFormation template)
- Library in different programming languages
- Including AWS Construct Library
- https://cdkworkshop.com
- https://github.com/awslabs/aws-cdk
11. ECS Deep Dive
- ECS and Fargate
- Containers get IP address from VPC (see below)
- Containers can get their own IAM role (see below)
- For service discovery, can use Route 53 DNS with ECS (not internal DNS like in Kubernetes)
- Fargate is a part of ECS (runs on ECS)
- ECS automatically schedules containers to nodes in the cluster
- Can be customised with parameters
- ECS agent and ECS AMI on each cluster node (must be installed)
- For ECS, you must provision and set up the EC2 instances for the cluster
- The ECS control plane is managed by AWS and free
- Run workloads on ECS by defining tasks that consist of one or more containers
- Works the same for Fargate
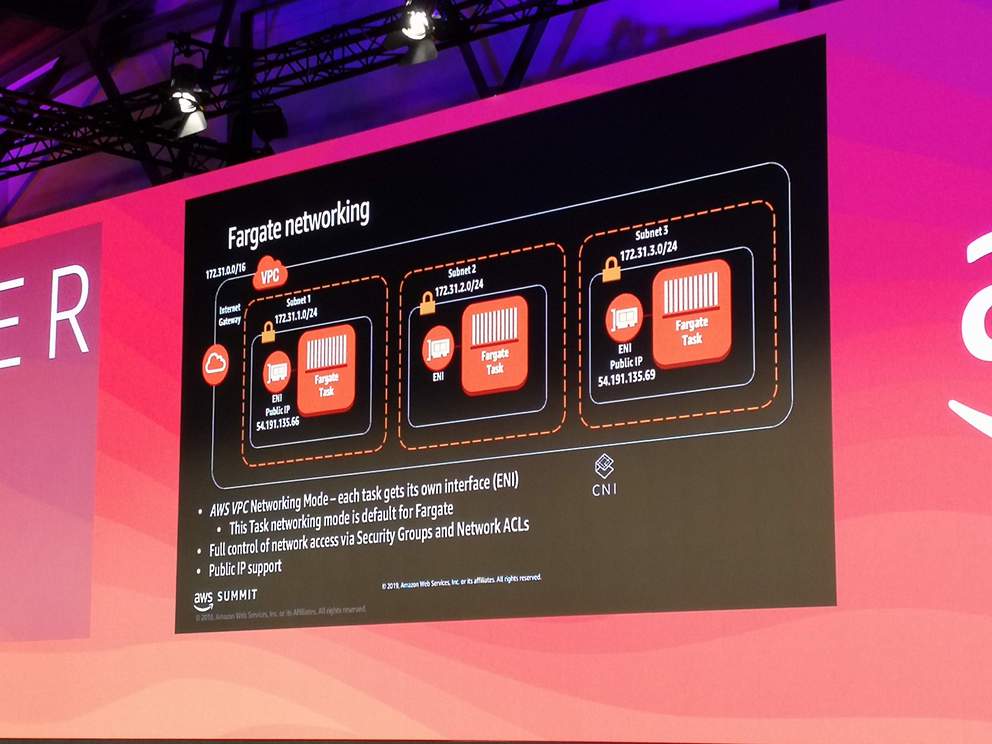
- Fargate networking
- VPC networking mode: each task runs in its own subnet with its own Elastic Network Interface (ENI)
- The VPC can be shared with other tasks and AWS services (e.g. Load Balancer)
- ENI needs internet access (to pull container images)
- VPC networking mode: each task runs in its own subnet with its own Elastic Network Interface (ENI)
- Fargate permissions
- Cluster permission: define who can run tasks with IAM policies
- Application permissions: reference IAM role from task definition
- Can define permissions on container-level by specifying IAM roles in task definitions
- Fargate logging
- Can define log configuration in task definition (for each container)
- https://gitlab.com/ric_harveybl_practical_fargate